Overview
As an engineer, you may find it challenging to test your code across multiple platforms and environments, which can lead to compatibility issues or bugs. Fortunately, GitHub Actions Matrix strategy can help you automate testing with different configurations and increase your test coverage.
What is the Matrix Strategy?
The matrix strategy is a feature in GitHub Actions that allows you to run a job with multiple configurations. For example, if you want to test your code with different versions of a programming language, you can create a matrix that runs your job with each version. A matrix can also be used to test your code on different platforms, environments, or with different parameters.
How does the Matrix Strategy work?
The strategy keyword is used to define a parallel strategy for your workflow and is used in conjunction with the matrix keyword, which allows you to define multiple combinations of inputs that should be run in parallel. The strategy keyword takes a single object, which can contain the following properties:
matrix: This property is used to define a matrix of inputs that should be run in parallel.
The matrix property takes an object, where the keys are the names of the inputs and the values are arrays of possible values for each input. Using the matrix keyword in this way can greatly improve the reliability of your workflow, as it allows you to test against a wide range of inputs and identify any potential issues before they are released to production. Another important aspect of the matrix is that its values are available and can be used in the steps of a job. Finally, it’s also worth noting that the matrix can be defined in multiple jobs, and it’s also possible to use it in conjunction with if statements to conditionally run certain jobs based on the matrix values.
-
fail-fast: This property is used to specify whether the workflow should fail as soon as one job fails. The default value is false, which means that the workflow will continue running even if one job fails. -
max-parallel: This property is used to specify the maximum number of jobs that should run in parallel.
Benefits of using a Matrix Strategy
This approach is useful for several reasons:
- Increased efficiency: With this strategy, you can optimize your workflow to run faster, by specifying how many jobs can run in parallel and what order they should run in.
- Increased coverage: You can test your code with multiple configurations, increasing the coverage of your tests and reducing the risk of errors.
- Better resource utilization: By controlling how many jobs can run in parallel, you can ensure that your workflow is not using more resources than necessary.
- Better insights: A matrix can provide insights into how your code performs under different configurations, which can help you identify performance issues or compatibility problems.
- Automation: A matrix can be used to automate testing on different configurations, reducing the amount of manual testing required.
Steps to implement a Matrix Strategy
Using a GitHub Actions strategy and matrix is a straightforward process. Here are the steps you need to follow:
-
Define your matrix: Before you can create a matrix, you need to define the configurations that you want to test. This can involve specifying things like different versions of a programming language, different platforms, or different parameters.
-
Create your matrix: Once you have defined your matrix, you can create it in your workflow file. You can specify the matrix in the “strategy” section of your workflow file.
-
Run your workflow: Once your strategy and matrix are defined, you can run your workflow. GitHub Actions will automatically execute your workflow according to your strategy and matrix, running your job with each configuration in the matrix.
Example
name: strategy-matrix
on:
workflow_dispatch:
jobs:
strategy-matrix:
# specify bash as default shell on all os
defaults:
run:
shell: bash
strategy:
max-parallel: 5
fail-fast: false
matrix:
os: [ubuntu-latest, windows-latest, macos-latest]
version: [8, 10, 12]
browser: [chrome, firefox, safari]
runs-on: ${{ matrix.os }}
steps:
- name: Print info
run: |
echo "OS:" ${{ matrix.os }}
echo "Version:" ${{ matrix.version }}
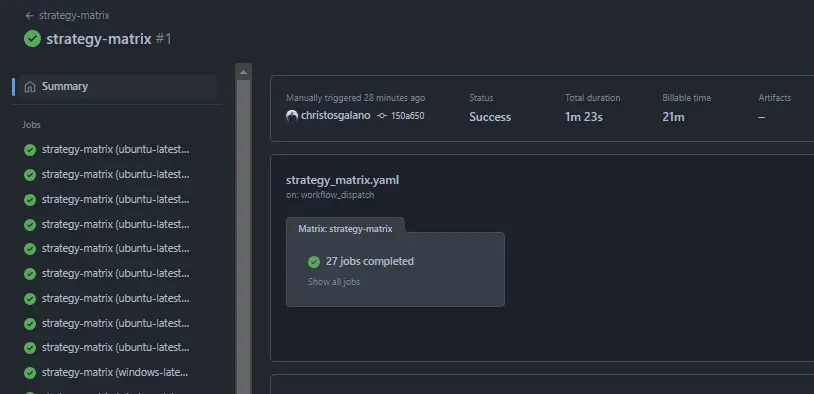
echo "Browser:" ${{ matrix.browser }}Here, the matrix specifies that the workflow should run on three different operating systems (ubuntu-latest, windows-latest, and macos-latest), three different versions (8, 10, and 12) and three different browsers (chrome, firefox, safari). This means that the workflow will run a total of 27 (3^3) combinations in parallel, rather than sequentially.
We also put a limit of 5 to how many jobs can run simultaneously by using max-parallel: 5.
Finally, we do not want all of the remaining jobs to be cancelled if a matrix-job fails, so we specify fail-fast: false.
Summary
The matrix strategy in GitHub Actions is a powerful feature that can help you optimize your CI/CD pipeline. By defining a matrix, you can test your code with multiple configurations, increasing coverage and reducing the risk of errors. It’s also a great way to automate testing on different configurations, saving you time and effort. If you’re not already using the matrix strategy, give it a try and see how it can improve your CI.


Leave a comment