Overview
Maintaining an active and well-organized codebase is crucial for the success of any project. However, repositories can become stale over time due to inactivity, resulting in outdated and irrelevant code within an organization’s GitHub structure. Addressing this problem manually can be labor-intensive, especially as the number of repositories grows. This is where the stale-repos action comes in. This action automates the identification of inactive repositories, allowing teams to maintain a clean and organized GitHub environment with minimal effort.
Risks of Inactive Repositories
Inactive repositories can lead to several issues within an organization, including:
- Security Risks: Outdated code may include unpatched vulnerabilities.
- Inefficiency: Active development teams may have to sift through numerous inactive repositories to find relevant projects.
- Confusion: Stale repositories can create ambiguity, making it harder for teams to distinguish active projects from abandoned ones.
Automating the identification of stale repositories allows organizations to mitigate these risks and streamline their repository management processes.
GitHub Action
The stale-repos action, developed by GitHub, offers a powerful solution for identifying and reporting inactive repositories within an organization.
This action benefits teams managing numerous repositories under a single GitHub organization, where keeping track of activity across all projects can become overwhelming. The stale-repos action identifies repositories with no activity for a configurable number of days and flags them for potential archival. The action was created by GitHub to help its internal teams maintain their open-source projects, and it has been made available as an open-source tool for the broader community.
For this action, a repository is considered inactive if it has not had a push in a configurable number of days. By default, the action checks for activity based on the repository’s push history. It can also be configured to evaluate activity based on the default branch by adjusting the ACTIVITY_METHOD variable. This flexibility allows teams to tailor the tool to their specific needs.
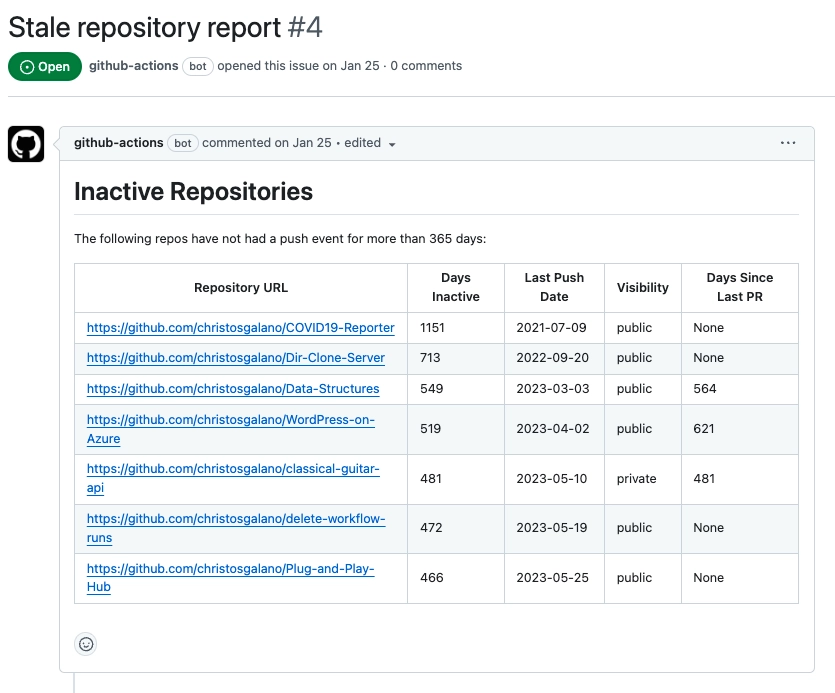
The action generates a report highlighting inactive repositories, helping teams decide which repositories should be archived or otherwise maintained. For organizations with many repositories, GitHub itself uses this action to archive repositories in batches, ensuring that their open-source projects remain well-maintained and relevant.
Usage Example
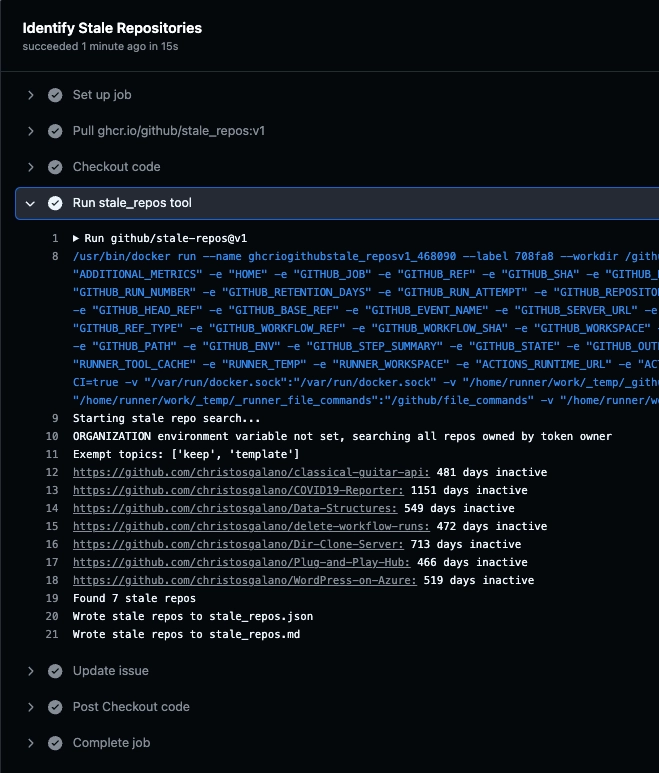
To demonstrate how this action can be used, below is an example workflow configured to run from my .github repository. This workflow runs on the first day of each month and automatically identifies repositories that have been inactive for over 365 days. Any repository marked as stale will be flagged for review, and the results will be posted in a GitHub issue within the same repository.
name: stale-repos-identifier
on:
workflow_dispatch:
schedule:
- cron: '0 0 1 * *' # At 00:00, on day 1 of the month
jobs:
identify:
name: Identify Stale Repositories
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
permissions:
contents: read
issues: write
steps:
- name: Checkout code
uses: actions/checkout@v4
- name: Run stale_repos tool
uses: github/stale-repos@v1
id: stale-repos
env:
GH_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.STALE_REPOS_TOKEN }}
EXEMPT_TOPICS: "keep,template"
INACTIVE_DAYS: 365
ACTIVITY_METHOD: "pushed"
ADDITIONAL_METRICS: "pr"
- name: Update issue
run: gh issue edit 4 --body-file stale_repos.md --repo ${{ github.repository }}
env:
GH_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}-
STALL_REPOS_TOKEN: This secret token has permission to read all repositories across the organization, allowing the action to access the necessary data for the stale check.
-
EXEMPT_TOPICS: This variable allows you to exclude specific repositories from the stale check based on their topics. For instance, repositories tagged as “keep” or “template” will not be flagged as stale, ensuring that reference or template repositories remain untouched.
-
INACTIVE_DAYS: This variable defines the period of inactivity after which a repository is considered stale. In this example, repositories with no activity for 365 days are flagged.
-
ACTIVITY_METHOD: This variable specifies the method used to determine activity. In this case, the action checks for the last push activity to identify stale repositories.
-
ADDITIONAL_METRICS: This variable specifies additional metrics to consider when evaluating repository activity. In this example, the action also checks for open pull requests (PRs) to provide a more comprehensive overview of repository activity.
Summary
Managing a growing number of repositories within an organization can be overwhelming. By automating the identification of inactive repositories, the stale-repos action ensures that your GitHub environment remains secure, organized, and efficient. Whether you are a small team or a large enterprise, implementing the above workflow will help you maintain a clean and healthy codebase, allowing you to focus on what matters most—building great software.


Leave a comment